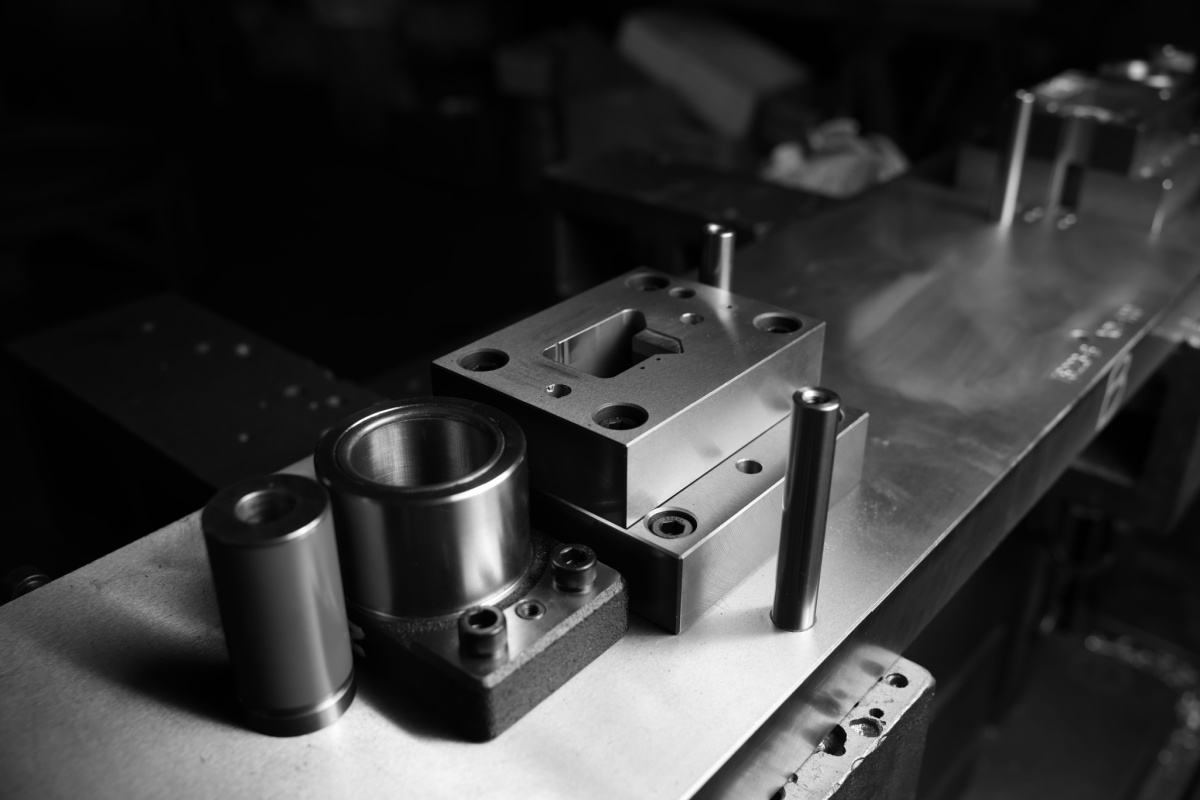
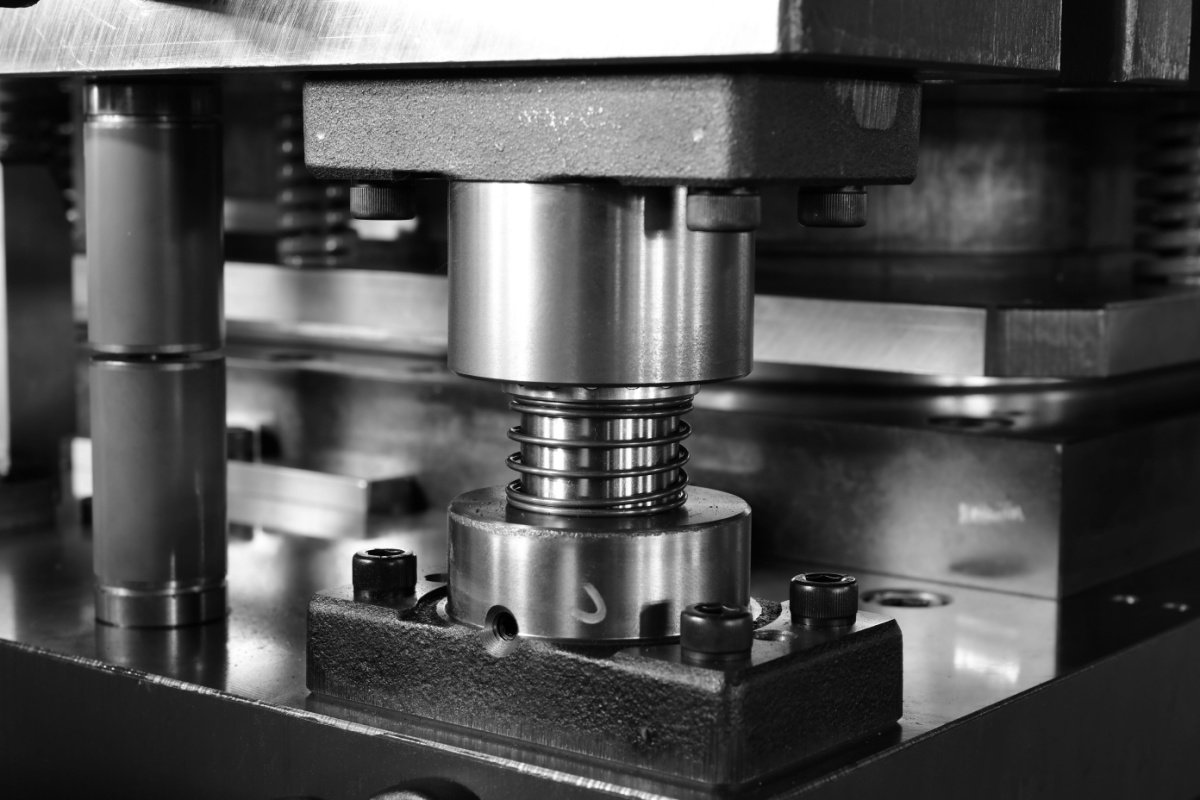
Drug delivery devices are becoming smaller and more complex for the safe and convenient administration of medication. Under the surface of these devices lies intricately formed wire components (springs, clips, actuators and more) that are engineered to exacting tolerances and robust enough to endure repeated use or long shelf lives. Precision bending is one of the most critical aspects of their design.
Medical engineers need a clear understanding of bending tolerances, how material selection and geometric accuracy fit in with wire forms and why a strategic approach to these factors is essential for scalable and compliant pharmaceutical manufacturing.
The importance of bending tolerances for medical wire forms
Tight bending tolerances are a non-negotiable feature in medical-grade wire forms. These devices often include features such as dose counters and internal actuation systems that must operate consistently within narrow physical constraints. A slight deviation in a wire’s bend angle or radius can lead to mechanical failures, which directly results in a higher rejection rate and difficulty in passing stringent medical trials.
Wire forms in these applications typically involve multi-axis bends that interact with plastic housings, springs or other metal inserts. Precision in bending ensures that these forms fit seamlessly within the device casing and maintain spring characteristics or actuation forces over time. On top of that it also helps these wire forms withstand repeated sterilisation without deformation.
Material selection as the foundation of performance
No matter how precise a bend is, the wrong material can compromise the wire form's function. Drug delivery devices face extreme demands like chemical exposure, bodily fluids, sterilisation cycles or long-term storage. The wire’s base material must offer the right balance of strength, corrosion resistance, ductility and manufacturability. Without the right material, scrap rates will rise and efficiency will fall.
Some of the most commonly used materials include:
- 304 or 302 stainless steel: These are go-to choices for their general strength and corrosion resistance. However, their springiness can make tight bends challenging unless tempered or work-hardened.
- Phosphor bronze: Excellent for applications needing corrosion resistance with moderate mechanical stress. It offers smoother bending but slightly less resilience under repeated stress.
- Nitronic alloys: Ideal for complex geometries. Nitronic offers higher strength and ductility, making it ideal for tightly bent or high-load applications within drug delivery devices.
The role of geometric accuracy and repeatability
As drug delivery devices evolve to meet ever-changing regulatory and customer demands, the wire forms inside them need to meet more complex requirements. Accuracy in three-dimensional geometry is especially crucial in wire forms that need to compress, extend, latch or align precisely with mating components.
Geometric accuracy in wire forms can be achieved through specialist tooling that is designed to maintain consistent angles and radii across large production volumes. Alongside this, automated bending equipment and in-line inspection systems can be used to continuously verify dimensional tolerances.
Manufacturers need to anticipate how a wire will behave during and after bending. Some metals exhibit spring-back, requiring over-bending to achieve the final desired angle. Managing this with predictability is critical to ensuring repeatability across batches.
Post-processing techniques to prevent deformation and ensure compliance
Wire forms need to be durable enough to maintain their precise form through post-processing steps like cleaning or electroplating. In drug delivery applications, surface finish and particulate-free manufacturing are an absolute necessity to meet regulatory requirements. Any deformation from post-processing can lead to non-compliance with medical standards. To combat this, manufacturers can use a number of techniques.
- Laser deburring to ensure ultra-smooth edges without risking deformation of ultra-thin wires.
- Carefully controlled surface finishes like passivation or electroplating, depending on the form’s function.
- Integrated design-for-manufacture principles, optimising the wire form’s geometry to minimise risk throughout the entire production process.
Partnering for medical wire form precision
Precision bending in wire forms is a multidisciplinary balance of material science and manufacturing expertise. In drug delivery devices where even a marginal deviation can result in failed trials or product recalls, getting this balance right from the outset is critical.
Advanex Medical provides end-to-end support in wire form design, prototyping, material selection and mass manufacturing. We help medical device designers develop robust and scalable wire form components that meet the industry's highest standards with in-house expertise and cutting-edge facilities.
To find out more about how precision-made wire forms can support your drug delivery innovations, download our guide below.